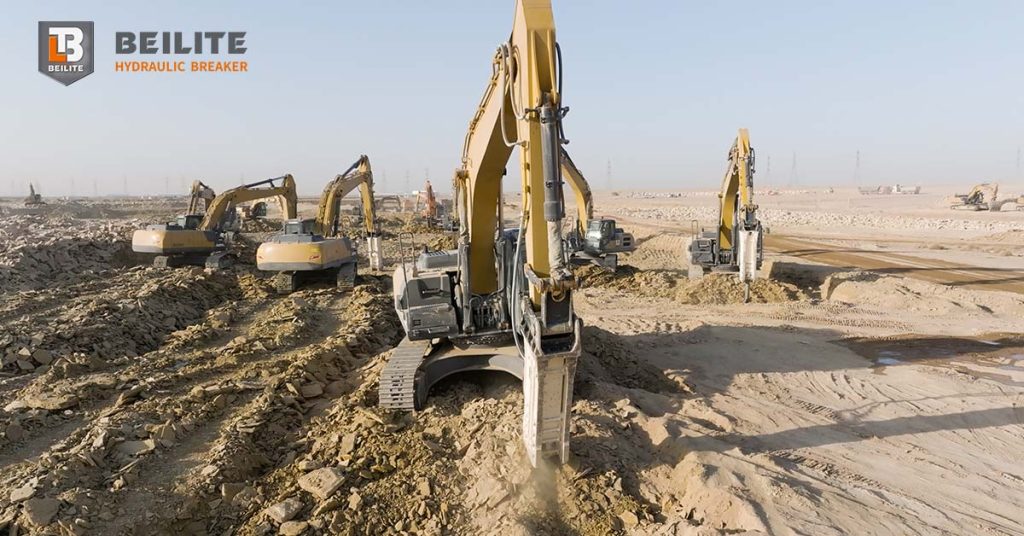
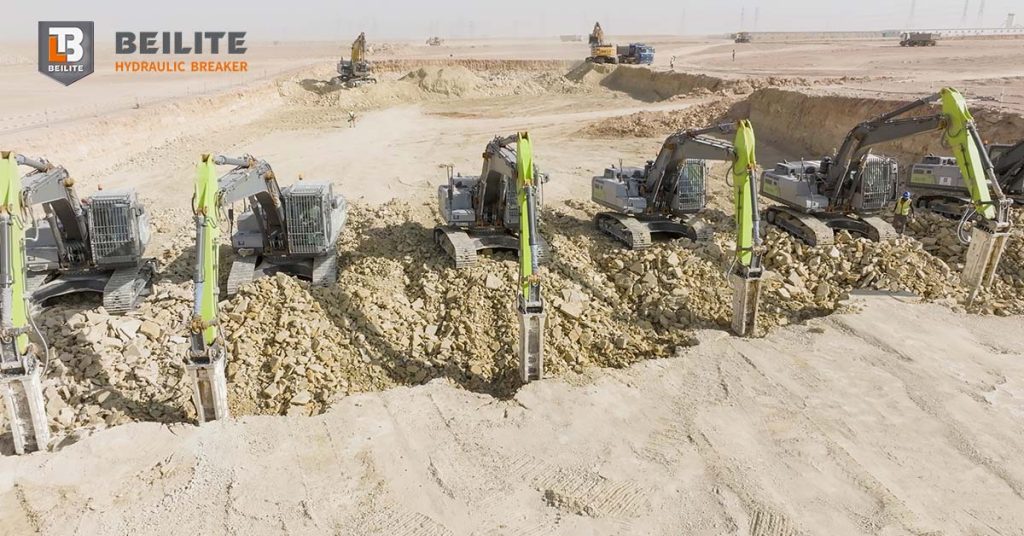
Choosing the right hydraulic concrete breaker for excavation is one of the most important decisions for contractors, builders, and heavy-equipment operators. Whether you are working on foundation excavation, trenching, concrete slab removal, underground utilities, or site preparation, the performance of your hydraulic breaker dramatically affects your project speed, cost, and safety. A well-matched hydraulic breaker delivers high impact power, reduces stress on the excavator, and ensures efficient breaking of concrete, rock, and compacted earth. Hydraulic breaker also known by hammer breaker, rock breaker, excavator breaker, and hydraulic concreate breaker. These terminologies are widely used by operators, engineers, and manufacturer to name a same tool.
As modern construction demands stronger equipment for deeper and more complex excavation work, the role of hydraulic breakers has expanded far beyond simple demolition. Today, hydraulic concrete breakers are used widely across excavation projects in urban infrastructure, mining development, rural roadworks, bridge foundations, and commercial building sites. This guide provides a clear, human-centered explanation of how to select the right hydraulic breaker for your excavator and how to ensure reliable performance on every job.
Understanding the Role of Hydraulic Concrete Breakers in Excavation
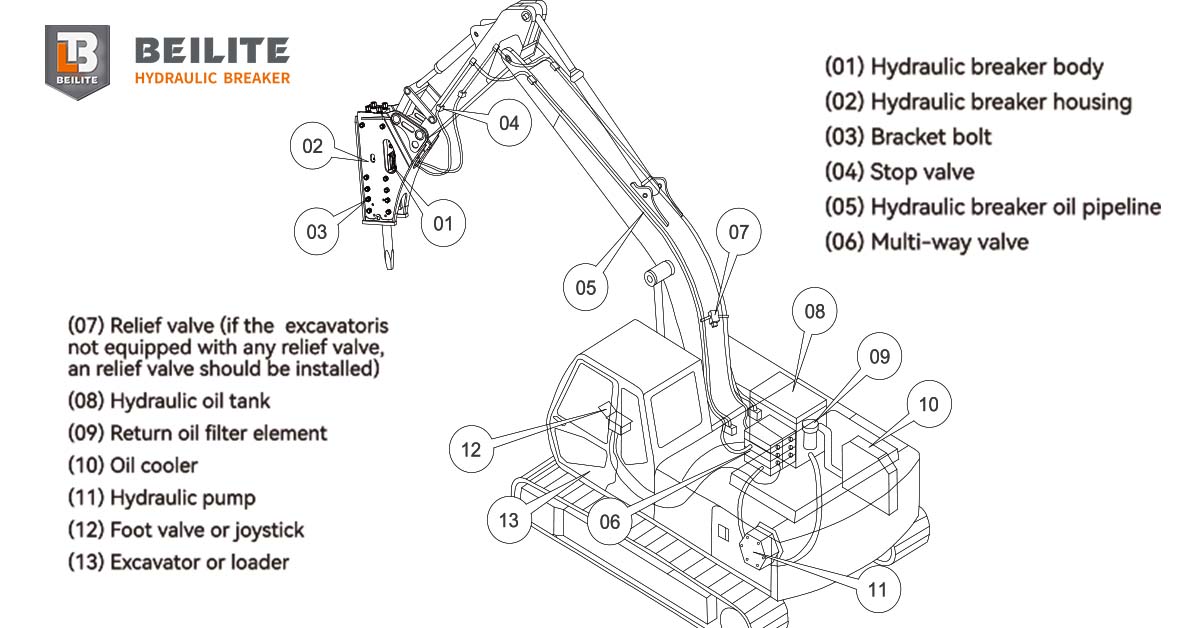
Excavation often involves more than just digging soil. Many sites contain old reinforced concrete, compacted rocky layers, boulders, pavement, and hardpan that standard buckets cannot penetrate. A hydraulic breaker converts hydraulic pressure into high-frequency impact energy, allowing the operator to fracture even the toughest materials. This significantly increases excavation efficiency, prevents damage to the excavator bucket, and improves site safety by reducing manual breaking.
Contractors working with foundation excavation, road construction, sewer line excavation, electrical trenching, and building demolition increasingly rely on a properly sized hydraulic hammer. A mismatched breaker, however, can slow productivity, increase fuel costs, and cause severe equipment damage. This is why correct selection is crucial.

Crucial to Match the Hydraulic Breaker to Excavator Size and Weight
One of the most important factors in choosing a hydraulic concrete breaker is ensuring the compatibility with the excavator’s operating weight and hydraulic flow. Hammer Breakers are engineered to work within specific oil flow ranges, oil pressure levels, and carrier weight classes. For example, a hydraulic breaker designed for a 20-ton excavator should not be used on a 30-ton machine, and vice versa. Undersized rock breakers may deliver weak impact force, while oversized rock breakers put stress on the excavator’s boom, pins, and hydraulic system.
Contractors should always check:
- Excavator operating weight
- Hydraulic oil flow (L/min)
- Hydraulic pressure (bar)
- Hydraulic Breaker chisel diameter and impact rate
Correct matching ensures balanced power transfer and smooth operations on rocky excavation sites.
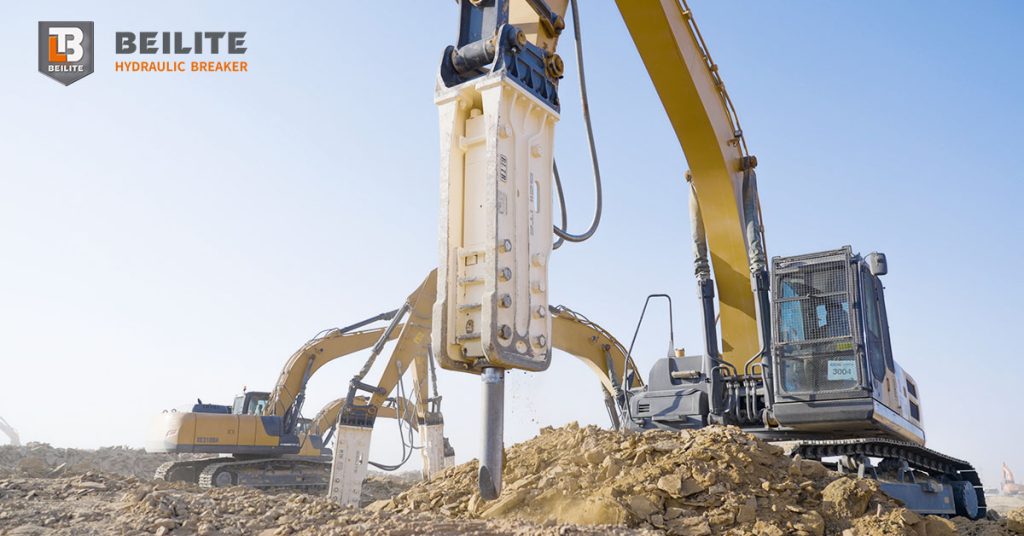
Choosing the Right hydraulic Breaker Type for Excavation Work
Different excavation jobs require different hammer breaker types. Noise-sensitive areas such as city centers, residential zones, and enclosed environments often benefit from silenced hydraulic breakers, which reduce operational noise while maintaining strong impact power.
Open-type or top-mounted breakers provide high striking force and easier access for maintenance, making them ideal for outdoor excavation, heavy concrete demolition, and rocky trenching. Side-mounted breakers offer improved lateral visibility and can be easier to maneuver when working close to walls or narrow excavation spaces.
Understanding your job requirements—whether you are breaking reinforced concrete slabs, trenching through hard rock, or loosening compacted soil, that will help you determine the best rock breaker design for the project.
Material Hardness and Hydraulic Breaker Performance
Excavation sites can vary dramatically. Some contain soft soil with occasional boulders, while others feature dense concrete, mixed debris, or solid bedrock. Harder materials require breakers with higher impact energy and tool durability.
For example:
Reinforced concrete foundation requires a hydraulic breaker with high blow energy and a strong chisel or moil point tool.
Rocky soil and hardpan benefit from conical or blunt chisels that distribute force deeper.
Granite and basalt excavation demand heavy-duty hydraulic hammers designed to withstand continuous high-impact work.
Selecting the right chisel type (tool) is just as important as selecting the hammer breaker itself, as tool shape affects penetration, cracking pattern, and breaking speed.
Beilite Hydraulic Breaker Durability, Construction Quality, and Service Support
A hydraulic concrete breaker used in excavation faces extreme working conditions such dust, vibration, shock load, and continuous impact cycles. The durability becomes a major consideration. Thick hammer breaker housings, well-tempered steel components, and high-precision pistons ensure long-term reliability.
Equally important is after-sales service and parts availability. Hydraulic breaker maintenance often includes seal kit replacement, chisel replacement, and periodic overhaul. Brands with strong aftermarket support and easily available spare parts help contractors reduce downtime and maintain productivity.
Key Points to Consider When Choosing a Hydraulic Concrete Breaker
When choosing a concrete breaker, look for features such as:
- High-quality piston and cylinder material
- Efficient energy recovery systems
- Anti-blank firing protection
- Reinforced front housing
- Easy disassembly for maintenance
These features improve performance and extend equipment life, especially in demanding excavation environments.
- Match breaker weight to excavator carrier size
- Check impact energy, oil flow, and blow frequency
- Choose the right chisel type for concrete or reinforced structures
- Select silent or side-type housing based on work environment
- Ensure easy parts availability and strong after-sales support
Safety and Maintenance Considerations
Appropriate regular maintenance is essential for safe and efficient excavation. Operators should follow recommended lubrication intervals, monitor chisel wear, and maintain clean hydraulic oil. Using the wrong oil or neglecting lubrication can cause internal scoring, overheating, and seal failure.
Daily inspections should check for leaks, unusual vibration, loose bolts, and chisel deformation. Training operators on correct positioning, avoiding blank firing, and selecting the right chisel type significantly improves breaker lifespan and performance.
Summary
A hydraulic concrete breaker for excavation is a powerful tool that transforms an ordinary excavator into a high-performance demolition and trenching machine. Selecting the right breaker involves evaluating excavator compatibility, material hardness, breaker type, durability, and service support. Investing the time to make the right choice will dramatically increase productivity and reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Whether you are working on residential excavation, commercial construction, quarry trenching, or infrastructure development, the right hydraulic breaker ensures clean, efficient, and safe breaking performance across all excavation conditions.
FAQs
1. How do I know which hydraulic concrete breaker is compatible with my excavator?
To choose the right breaker, always match the breaker operating weight and oil flow requirement with your excavator’s specifications. Each excavator has a recommended hydraulic hammer range. If the breaker is too small, it won’t deliver enough impact energy for concrete demolition. If it’s too large, it may overload your boom, dipper arm, and hydraulic pump. Check your excavator’s manual and compare it with the breaker’s oil flow (L/min), working pressure (bar), and tool diameter.
2. How often should I maintain a hydraulic breaker during excavation work?
Maintenance depends on jobsite conditions, but most breakers require greasing every 2–5 hours of continuous use, especially when breaking reinforced concrete or thick slabs. Operators should inspect the front bushings, chisel, nitrogen pressure, and side bolts daily. Regular checks prevent piston scoring, overheating, and seal failure. Using clean hydraulic oil and proper lubrication significantly extends the hammer’s life.
3. What type of chisel is best for concrete excavation and demolition?
For most concrete excavation tasks, a moil point (cone) is ideal for deep penetration and cracking hard surfaces. For large concrete slabs, asphalt, and trench excavation, a flat or wide chisel delivers better breaking force and efficiency. The correct tool bit reduces stress on the piston, bushings, and excavator, ensuring smoother hammering and faster work progress.
Beilite Machinery Co., Ltd.
40008-40008
info@beilite.com
+6282321982255

 English
English Indonesian
Indonesian